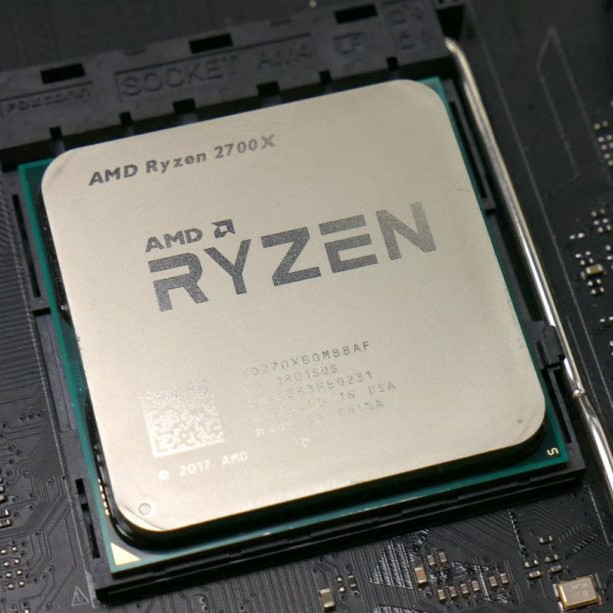
A central processor, or CPU, is arguably the most important component of any computing device. It handles basic instructions and allocates the more complicated tasks to other specific chips to get them to do what they do best. It’s the core of your PC, smartphone, or tablet. and it’s what makes the whole device run as it should.
The CPU itself is a core component of what makes a computer a computer, but it isn’t the computer itself — it’s just the brains of the operation. It’s a small computer chip that sits atop the main circuit board (motherboard) of a computer, whether that’s a desktop PC, laptop, or tablet. It’s distinctly separate from the memory, which is where information is stored, and the graphics card or graphics chip, which handles all rendering of video and 3D graphics to your monitor or screen.
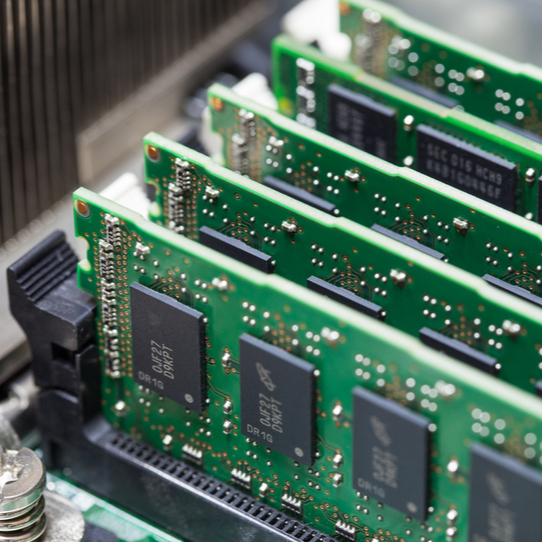

Alternatively referred to as main memory, primary memory, or system memory, RAM (random-access memory) is a hardware device that allows information to be stored and retrieved on a computer. RAM is usually associated with DRAM, which is a type of memory module. Because information is accessed randomly instead of sequentially like it is on a CD or hard drive, access times are much faster. However, unlike ROM, RAM is a volatile memory and requires power to keep the data accessible. If the computer is turned off, all data contained in RAM is lost.
Over the evolution of the computer, there have been different variations of RAM. Some of the more common examples are DIMM, RIMM, SIMM, SO-DIMM, and SOO-RIMM. Below is an example image of a 512 MB DIMM computer memory module, a piece of RAM found in older desktop computers. This memory module would be installed into one of the memory slots on a motherboard.
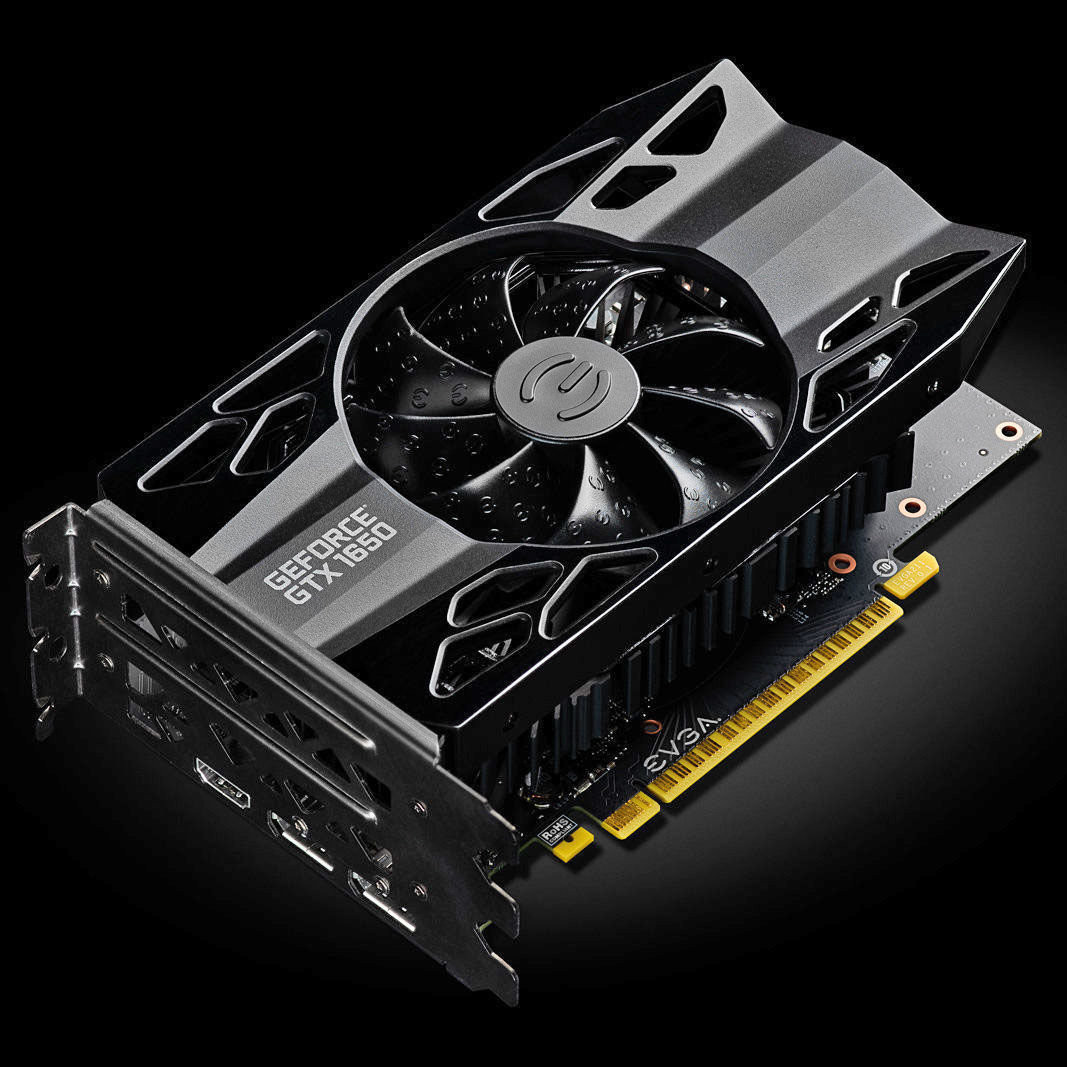

GPU stands for graphics processing unit. You’ll also see GPUs commonly referred to as graphics cards or video cards. Every PC uses a GPU to render images, video and 2D or 3D animations for display. A GPU performs quick math calculations and frees up the CPU to do other things. Whereas a CPU uses a few cores focused on sequential serial processing, a GPU has thousands of smaller cores made for multi-tasking.
There are two different types of GPUs:
- Integrated GPUs are located on a PC’s CPU and share memory with the CPU’s processor.
- Discrete GPUs live on their own card and have their own video memory (VRAM), so that the PC doesn’t have to use its RAM for graphics.
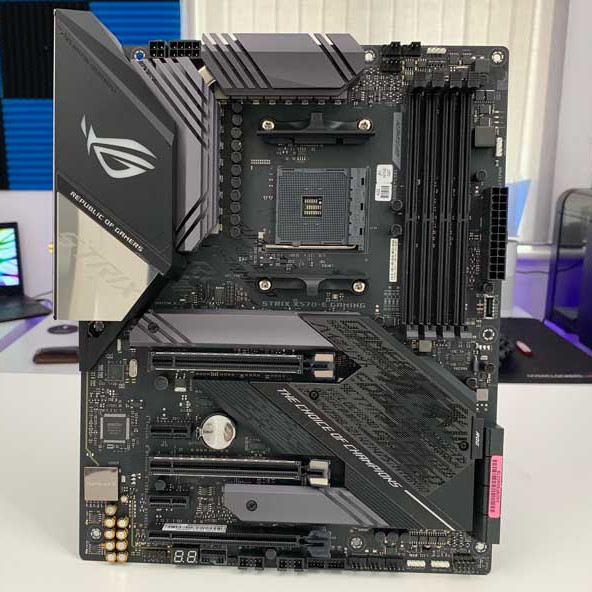

Alternatively referred to as the mb, mainboard, mboard, mobo, mobd, backplane board, base board, main circuit board, planar board, system board, or a logic board on Apple computers. The motherboard is a printed circuit board and foundation of a computer that is the biggest board in a computer chassis. It allocates power and allows communication to and between the CPU, RAM, and all other computer hardware components.
A motherboard provides connectivity between the hardware components of a computer, like the processor (CPU), memory (RAM), hard drive, and video card. There are multiple types of motherboards, designed to fit different types and sizes of computers.
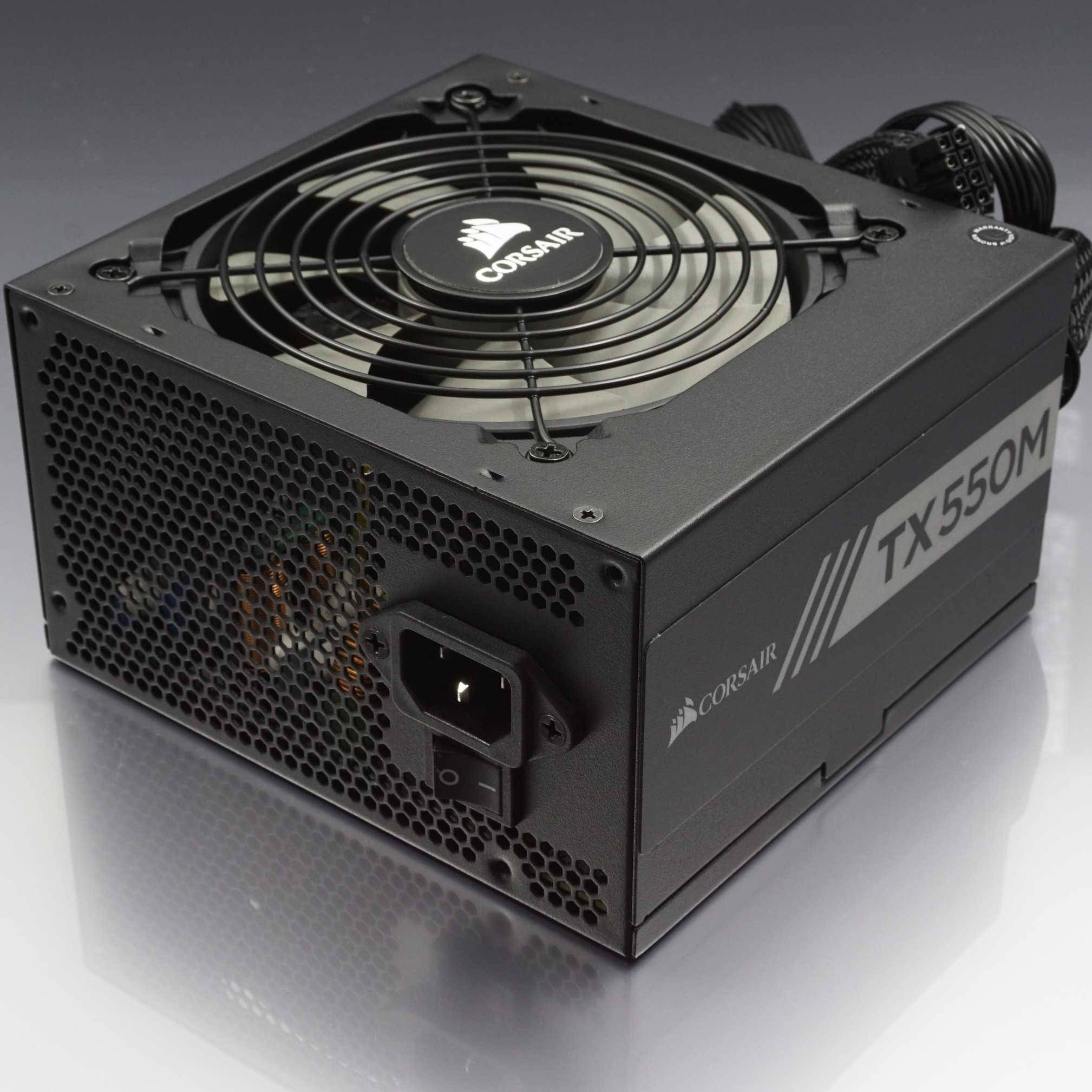

The power supply unit is the piece of hardware that converts the power provided from the outlet into usable power for the many parts inside the computer case.
It converts the alternating current from your wall outlet into a continuous form of power called direct current that the computer components require. It also regulates overheating by controlling voltage, which might change automatically or manually depending on the power supply.
The power supply is a crucial piece because, without it, the rest of the internal hardware can't function. Motherboards, cases, and power supplies all come in different sizes called form factors. All three must be compatible to work properly together.
YOUR
AD
HERE